Lidar annotation services from Tribotz support machine learning, artificial intelligence, and data operation techniques.
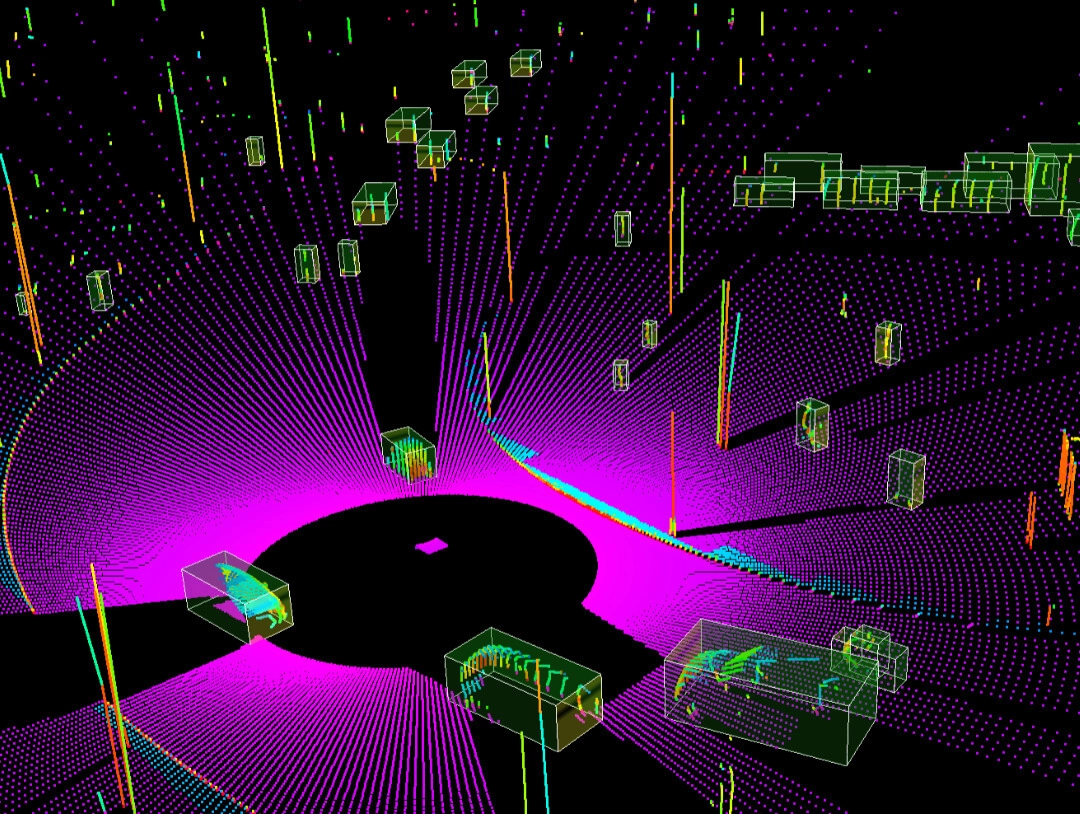
For many industrial applications, including geospatial technology and autonomous technology, LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) data is a crucial sensor. Lidar calculates distances to a given object using lasers, scanners, and specialised GPS receivers. Lidar data annotation is a difficult and time-consuming task that requires a high level of expertise in data annotation. Lidar annotation can be used in conjunction with picture annotation to build deep-learning models for computer vision and other applications.
Tribotz professionals have decades of combined expertise processing thousands of data points and are trained in annotating Lidar point cloud data. In order to meet a client’s project demands, Tribotz offers a variety of Lidar data labelling services, such as semantic annotation, 3D cuboid/box annotation, landmark annotation, polygon annotation, and polyline annotation. The team at Tribotz offers a full-service annotation platform and creates unique automation processes for clients after determining their throughput and quality standards.
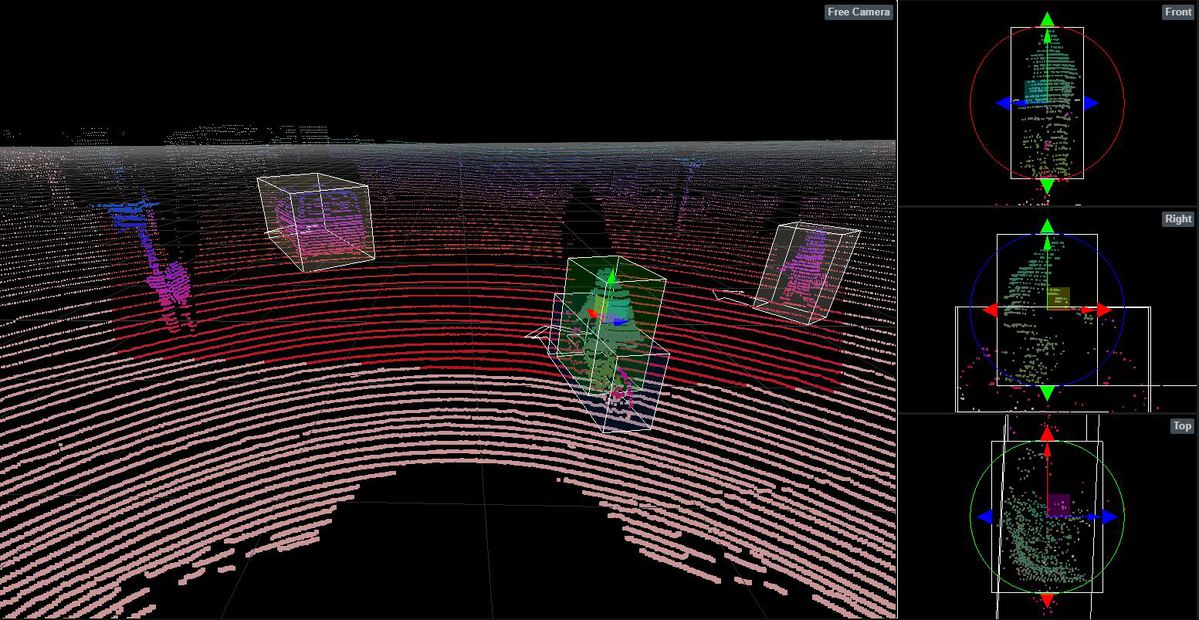
Autonomous vehicles use LIDAR box labelling to recognise items in 3D pictures. Machines learn to quickly recognise labelled things within a given area through the use of 3D Lidar sensor data.
Lidar polygon annotations, which are pixel-perfect polygons that are precisely drawn around the object of interest, are useful for training object localization & identification algorithms for objects like logos, signboards, and various human postures.
Machine learning algorithms can recognise tiny images because Lidar landmark annotation marks anatomical or structural sites of interest to produce precise datasets determining the shape of various-sized objects.
Through 3D point cloud annotation, fine-grained features may be recorded, enabling models to carry out object detection and separate various 3D objects in a scene.
One of the fundamental components of autonomous technology is LIDAR semantic segmentation, which assigns a class label to each input modality data point.
Autonomous vehicles can discern street lanes across roads in cities and on highways with the use of LIDAR polyline annotation. To make the road structure readily recognised to self-driving automobiles, Tribotz's labellers mark raw data and photographs of city streets and highways.
You will be guided by Tribotz subject matter experts as you create a unique end-to-end workflow.
Transformational, problem-solving strategy. Addressing problems with LIDAR annotation across disciplines. Agility and responsiveness are two factors that improve Time to value.
Specific resources Customized skill. Curriculum for focused and in-depth microlearning. Domain knowledge Rostering equipment.
Lidar annotation tools and procedures alignment. Developmental Milestones with Structure. Two-step QA annotation and production processes
Analytical transparency. Real-time monitoring and insights about service delivery. Improving Dynamic Models from Edge Case Perspectives.
Evaluation of the deliverable evaluation of crucial indicators and quality assurance procedures. Reconsidering the model. Analysing company results.
To detect the road, identify objects, and differentiate between passing landscape and potentially dangerous items, AV uses a combination of three types of sensors: cameras, laser-based Lidar, and conventional 2D radar.
Machine learning algorithms in agriculture can be trained using Lidar training data to pinpoint locations that need more water or fertiliser. Farmers who use this information stand to save money, time, and labour.
Governmental organisations employ LIDAR technology in many different ways. Intelligence agencies employ it to protect a straight line of sight and clear built-up areas frequented by high-risk individuals.

At Tribotz, we specialize in developing advanced AI and Machine Learning Data solutions that help businesses unlock the full potential of their data. Our team of experienced data scientists and engineers work with clients to develop customized solutions that address their unique data challenges and enable data-driven decision making.